We’ve gathered data and facts on masturbation and its relationship with testosterone to answer the most common question: Does masturbation decrease testosterone?
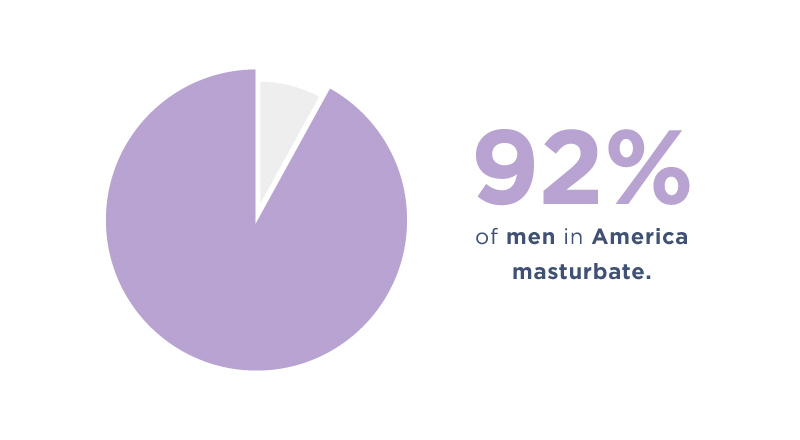
Masturbation is fairly common all over the world for both men and women.
It’s sometimes stigmatized for a variety of reasons. Some say that masturbation decreases testosterone, but is that really backed up by science?
In this article, we’ve gathered current data and statistics around masturbation, its relationship with testosterone in both men and women, and what might cause low testosterone levels.
Let’s dive in:
Top Masturbation & Testosterone Statistics You Should Know:
- 84% of Americans and 92% of men in America masturbate.
- One study found a significant increase in plasma levels of testosterone, along with other steroid hormones, after men masturbated.
- Sexual arousal from masturbation produced a noticeable increase in plasma testosterone in women.
- When women had an orgasm, there was also a slight increase in testosterone concentrations.
- Another study saw no changes in testosterone levels after masturbation following a 3-week abstinence period. Masturbation didn’t affect testosterone.
- One study saw a significant increase in base testosterone levels after 3 weeks of abstaining from sex or masturbation.
- There was a 145.7% increase in testosterone levels after 7 days of abstinence in another study.
- Testosterone levels naturally begin declining by about 1% per year, from around age 30 onwards.
- There was a 35% average increase in testosterone levels after watching porn in one study.
Prevalence of Masturbation in America
Before we dive into whether or not masturbation affects your testosterone levels, first, let’s review the stats around how many people masturbate:
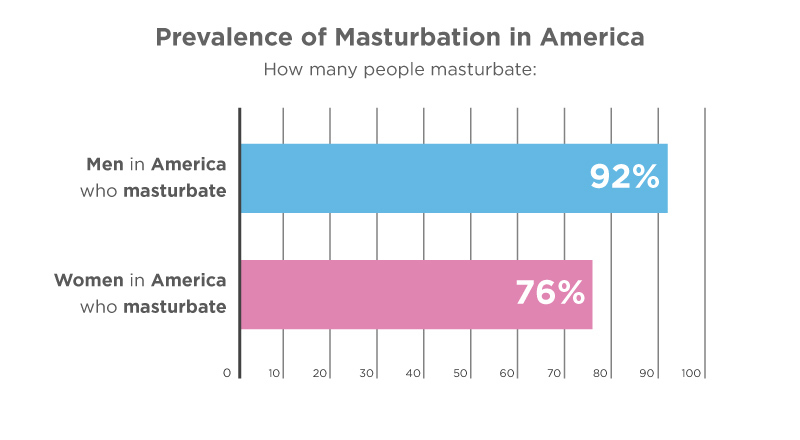
- 84% of Americans masturbate. (Tenga (Archived), 2018)1
- 92% of men in America masturbate.
- 76% of women in America masturbate.
- In a study of 226 male and female students, they reported their masturbation frequency: (Robert Morris University, 2010)2
- “Never masturbated”: 35% (79)
- “Less than once per month”: 13.7% (31)
- “1-3 per month”: 12.4% (28)
- “1 per week”: 7.1% (16)
- “2-3 per week”: 13.3% (30)
- “4-6 per week“: 9.3% (21)
- “Daily”: 5.3% (12)
- “More than once daily”: 3.5% (8)
Interested to know more details about the benefits of masturbation? Consider checking out our research study here.
Does Masturbation Decrease Testosterone?
These studies have reviewed whether testosterone increased, decreased, or stayed the same after masturbation. Here’s what they found:

- What is Testosterone? (Healthline, 2021)3
- Testosterone is a hormone found in humans and animals. It’s primarily produced by the testicles in men. Women’s ovaries also produce some testosterone, but the amounts are significantly smaller.
- Testosterone plays an important role in sperm production and is frequently associated with sex drive.
- Testosterone also has an effect on bone and muscle mass, how men store fat and red blood cell production.
- Some studies point to masturbation increasing testosterone in men:
- 2 out of 3 studies (below) indicate that masturbation increases testosterone. (Human Nature, 2006)4
- One of these studies measured plasma levels of testosterone before and after masturbating.
- They found a significant increase in plasma levels of testosterone, along with other steroid hormones, after masturbation.
- Plasma testosterone levels were correlated to DHT and oestradiol (the two steroid hormones that increased) but were not correlated with other steroid hormones. (Journal of Endocrinology, 1976)5
- In the second study on women, sexual arousal from masturbation produced a noticeable increase in plasma testosterone.
- When women had an orgasm, there was also a slight increase in testosterone concentrations. (Psychosomatic Medicine, 1999)6
- The third study saw no changes in testosterone levels after masturbation following a 3-week abstinence period. Masturbation didn’t affect testosterone. (World Journal of Urology, 2001)7
- Another study found no significant change in testosterone in the blood after masturbating to orgasm.
- Participants’ blood was analyzed before, during, and after masturbation-induced orgasm and found that testosterone, along with other endocrine variables, wasn’t significantly affected by sexual arousal and orgasm. (Psychoneuroendocrinology, 1998)8
These studies might not be conclusive, but it doesn’t look like masturbation decreases testosterone in men or women, and in some cases, it might actually increase it!
So, Does Abstaining Increase Testosterone?
If masturbation doesn’t have a significant effect on testosterone, does that mean it can be increased by not masturbating? Here’s what these studies found:
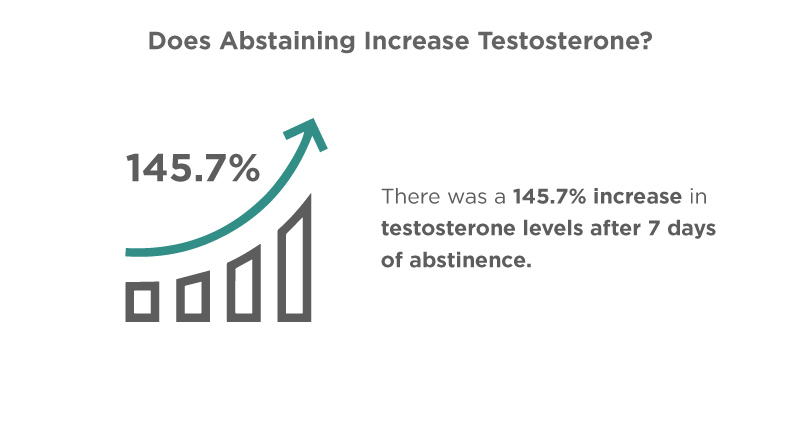
- One study saw a significant increase in base testosterone levels after 3 weeks of abstaining from sex or masturbation.
- Testosterone levels increased overall after the 3-week abstinence period. (World Journal of Urology, 2001)7
- There was a 145.7% increase in testosterone levels after 7 days of abstinence in another study. (Journal of Zhejiang University – Science A: Applied Physics & Engineering, 2003)9
- Testosterone changes from the 2nd to 5th day of abstinence were minimal and peaked by day 7. After this peak, testosterone levels remained relatively stable during continued abstinence.
So while masturbating might not decrease your testosterone further if you currently masturbate – it seems like stopping can increase it.
What Causes Testosterone to Drop?
Masturbation might not be causing low testosterone levels. Instead, testosterone can drop from a variety of other issues, ailments, or even just from getting older. Here’s what studies have shown:
- Low testosterone levels can be caused by a condition known as male hypogonadism, which is when the testicles (the male reproductive glands) do not produce enough testosterone. (Cleveland Clinic, 2018)10
- Testosterone levels naturally begin declining by about 1% per year, from around age 30 onwards. (Cleveland Clinic, 2018)10
- Other potential causes of low testosterone include: (Cleveland Clinic, 2018)10
- Injury (trauma, interrupted blood supply to the testes) or infection of the testes (orchitis)
- Chemotherapy for cancer
- Metabolic disorders such as hemochromatosis (too much iron in the body)
- Dysfunction or tumors of the pituitary gland
- Medications such as opioids, hormones used to treat prostate cancer, and steroids (such as prednisone)
- Acute (short-term) or chronic (long-term) illness
- Alcohol abuse
- Cirrhosis of the liver
- Chronic renal (kidney) failure
- HIV/AIDS
- Inflammatory conditions such as sarcoidosis (a condition that causes inflammation of the lungs and other organs)
- Kallman syndrome (abnormal development of the hypothalamus, a gland in the brain that controls many hormones)
- Klinefelter syndrome (a genetic condition in which a male is born with an extra copy of the X chromosome) – also called XXY syndrome
- High levels of the milk-producing hormone prolactin
- Obesity or extreme weight loss
- Uncontrolled type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Congenital defects present at birth
- Obstructive sleep apnea
- Aging
- Estrogen excess (usually from an external or environmental source)
- Previous anabolic steroid abuse
- Severe primary hypothyroidism
- Pubertal delay
- Trauma (such as a head injury)
- Radiation exposure or prior surgery of the brain
- Low testosterone levels in women can be caused by the ovaries being removed, as well as diseases of the pituitary, hypothalamus, or adrenal glands. (Healthline, 2021)3
Signs of Low Testosterone Levels
If you’re feeling the following symptoms, you might have low testosterone (and should consider consulting a doctor).
- Symptoms of low levels of testosterone among men include: (Healthline, 2021)3
- Decreased sex drive
- Less energy
- Weight gain
- Feelings of depression
- Moodiness
- Low self-esteem
- Less body hair
- Thinner bones
- Symptoms of low levels of testosterone among women include: (Healthline, 2021)3
- Low libido
- Reduced bone strength
- Poor concentration
- Depression
Does Watching Pornography Affect Testosterone?
Many men (and some women!) watch porn when they masturbate, so naturally, you might wonder if watching porn can affect testosterone levels. Here’s what studies have found:
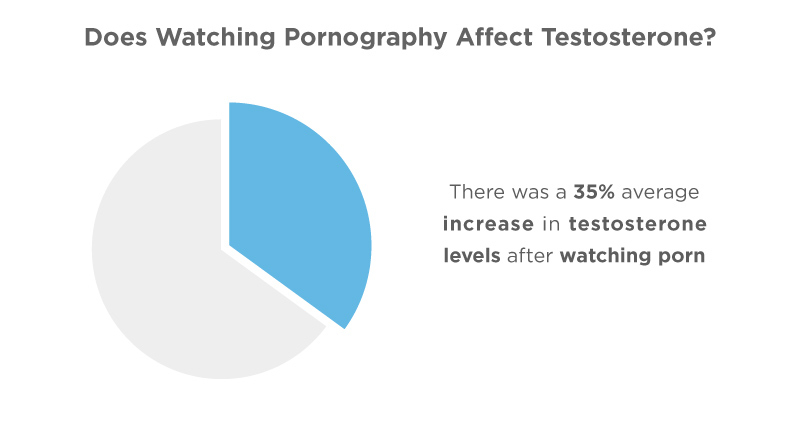
- 4 out of 5 studies found that watching erotic movies increases testosterone levels. (Human Nature, 2006)4
- There was a 35% average increase in testosterone levels after watching porn in one study. (Archives of Sexual Behavior, 1974)11
- This study measured plasma testosterone levels every 15 minutes for 3.5 hours before, during, and after the sexually explicit movie.
- The largest testosterone concentration was observed 60-90 minutes after the end of the film.
- No increase in testosterone was found in the participants who saw a sexually neutral film.
- Testosterone in saliva increased 15 minutes after men started watching porn in another study. (Psychoneuroendocrinology, 1985)12
- The concentration of testosterone in the saliva was studied among 20 young adult and healthy men before, during, and after the presentation of 5 different films. One was erotic, one sexual, one aggressive, one stressful, and one neutral.
- Testosterone levels increased 15 minutes after the beginning of the erotic and sexual films but decreased during the stressful film showing a dental surgery.
- Testosterone did not seem to change during either the neutral or the aggressive films.
- No differences were found between saliva testosterone levels before and after showing any of the films.
- Testosterone blood levels increased within the first 10 minutes of sexual arousal when watching a sexually arousing film compared to a sexually neutral film. (Psychoneuroendocrinology, 1993)13
Curios to know how many people watch porn? Check out our study here.
Will Masturbation Affect My Physical Performance?
Testosterone in men is associated with muscle mass, bone density, and overall strength. So if you’re hoping to get more gains at the gym, you might be wondering – should you stop masturbating?
Research is sparse on this topic, unfortunately, but there may be some anecdotal evidence from athletes and bodybuilders:
- Athletes and bodybuilders can have some conflicting opinions on this topic. Some claim that masturbation has had a negative impact on their performance, and others say it gives them an edge. (Healthline, 2018)14
- Unfortunately, no significant scientific evidence points out one way or the other. Current research on whether masturbation decreases physical performance is too limited to draw conclusions. (Healthline, 2018)14
Conclusion
So, does masturbation decrease testosterone levels?
Based on this research – it kind of depends on your perspective. It seems that abstaining from sexual activity increases testosterone levels – but if you’re currently masturbating, then more masturbation probably doesn’t make much of a difference.
Studies are still fairly sparse on this topic, though, so it may be worth experimenting on your own and seeing what feels best.
For more interesting sex studies and statistics, check out our guide here.
Footnotes
- Tenga (Archived), 2018. A survey of 13,000 men and women aged 18-74 across 18 countries.
- Robert Morris University, 2010. A study of 226 American male and female students at Robert Morris University.
- Healthline, 2021. An article on what testosterone is.
- Human Nature, 2006. A study on effects of social contexts and behaviors on sex steroids in humans.
- Journal of Endocrinology, 1976. A study of a group of young and healthy males.
- Psychosomatic Medicine, 1999. A study of 10 healthy female volunteers from Germany.
- World Journal of Urology, 2001. A study of 10 healthy male German volunteers.
- Psychoneuroendocrinology, 1998. A study of 10 healthy male Germans.
- Journal of Zhejiang University – Science A: Applied Physics & Engineering, 2003. A study of 28 male Chinese volunteers.
- Cleveland Clinic, 2018. An article on low testosterone.
- Archives of Sexual Behavior, 1974. A study of 8 male subjects.
- Psychoneuroendocrinology, 1985. A study of 20 young adults and healthy men from Germany.
- Psychoneuroendocrinology, 1993. A study of 9 healthy young males from France.
- Healthline, 2018. An article on masturbation can affect their physical performance.